www.joiiup.com
【運動】為什麼你該重量訓練(二)有病治病,沒病強身

撇除史考特不熟悉的中藥不談,我不曾聽說過有任何一種藥物是「有病治病,沒病強身」的。癌症需要化療藥治療、感染需要抗生素、高血壓要降血壓藥,但這幾種藥物對沒病的健康人來說,絕對沒有強身的功效,只有副作用的風險。
絕大多數宣稱有健康功效的保健食品,也都沒有治療疾病的功效。
就我所知,重量訓練是唯一符合「有病治病,沒病強身」的好東西。如果有一天我能把重量訓練當成藥物開立,那麼它絕對是我最常處方的藥物。

圖片來源:Dr.史考特的一分鐘健身教室
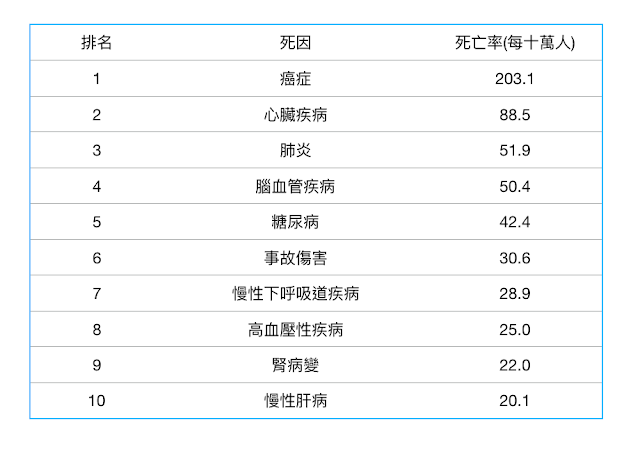
圖片來源:Dr.史考特的一分鐘健身教室
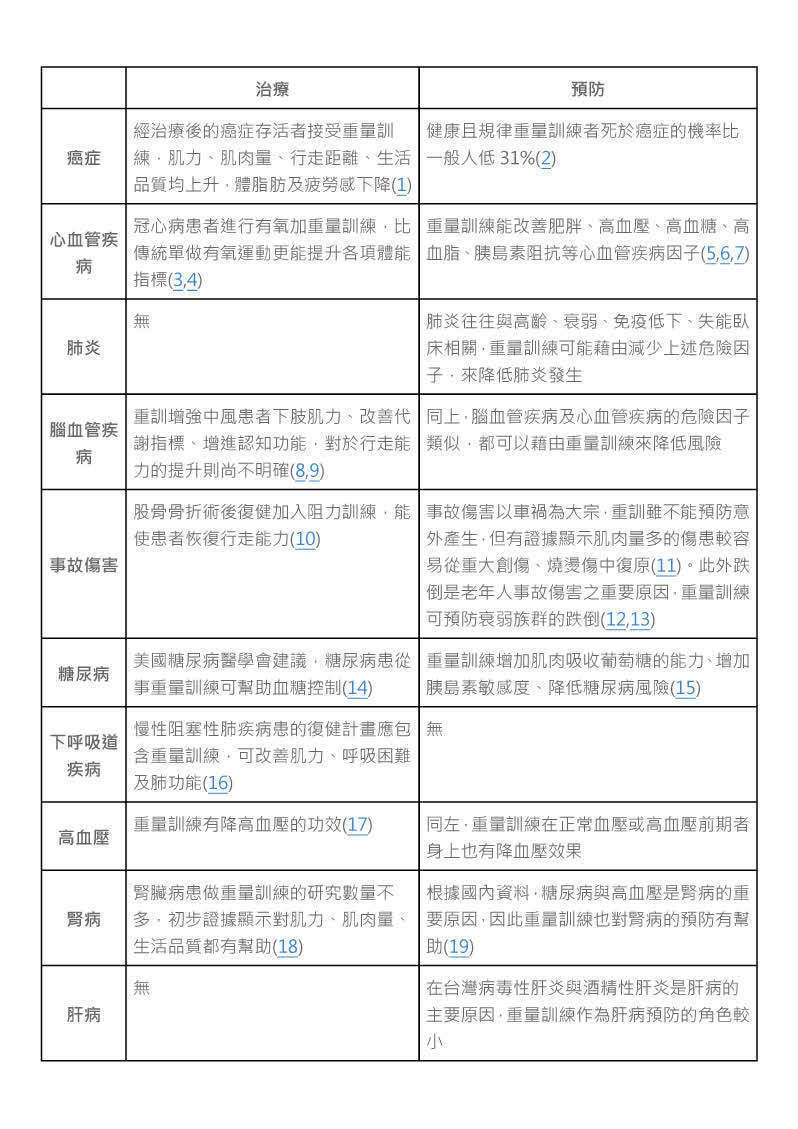
(失智症並不在十大死因內,是因為失智很少直接造成病患死亡,反而是失能所造成的續發性問題如營養不良、吞嚥困難、褥瘡等。運動與重量訓練同時有治療及預防失智的功效,我過去在這個影片中有詳細討論。)
結語
十大死因中,僅有肺炎與肝病完全無法藉由重訓預防或治療,沒有任何一種已知的藥物或健康食品,有如此廣泛的適應症。如果各位自認為熱愛生命,都應該開始向最近的健身房報到。
參考資料
Strasser B, Steindorf K, Wiskemann J, Ulrich CM. Impact of resistance training in cancer survivors: a meta-analysis. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2013;45(11):2080-2090.
Stamatakis E, Lee IM, Bennie J, et al. Does Strength-Promoting Exercise Confer Unique Health Benefits? A Pooled Analysis of Data on 11 Population Cohorts With All-Cause, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Mortality Endpoints. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187(5):1102-1112.
Marzolini S, Oh PI, Brooks D. Effect of combined aerobic and resistance training versus aerobic training alone in individuals with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Eur J Prev Cardiol. 2012;19(1):81-94.
Yamamoto S, Hotta K, Ota E, Mori R, Matsunaga A. Effects of resistance training on muscle strength, exercise capacity, and mobility in middle-aged and elderly patients with coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis. J Cardiol. 2016;68(2):125-134.
Ho SS, Dhaliwal SS, Hills AP, Pal S. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic, resistance or combination exercise training on cardiovascular risk factors in the overweight and obese in a randomized trial. BMC Public Health. 2012;12:704.
Kerksick C, Thomas A, Campbell B, et al. Effects of a popular exercise and weight loss program on weight loss, body composition, energy expenditure and health in obese women. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2009;6:23.
Cornelissen VA, Fagard RH, Coeckelberghs E, Vanhees L. Impact of resistance training on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension. 2011;58(5):950-958.
Gambassi BB, Coelho-Junior HJ, Schwingel PA, et al. Resistance Training and Stroke: A Critical Analysis of Different Training Programs. Stroke Res Treat. 2017;2017:4830265.
Wist S, Clivaz J, Sattelmayer M. Muscle strengthening for hemiparesis after stroke: A meta-analysis. Ann Phys Rehabil Med. 2016;59(2):114-124.
Sylliaas H, Brovold T, Wyller TB, Bergland A. Progressive strength training in older patients after hip fracture: a randomised controlled trial. Age Ageing. 2011;40(2):221-227.
Wolfe RR. The underappreciated role of muscle in health and disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 2006;84(3):475-482.
Buchner DM, Cress ME, de Lateur BJ, et al. The effect of strength and endurance training on gait, balance, fall risk, and health services use in community-living older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 1997;52(4):M218-224.
Liu-Ambrose T, Khan KM, Eng JJ, Janssen PA, Lord SR, McKay HA. Resistance and agility training reduce fall risk in women aged 75 to 85 with low bone mass: a 6-month randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2004;52(5):657-665.
Colberg SR, Sigal RJ, Yardley JE, et al. Physical Activity/Exercise and Diabetes: A Position Statement of the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care. 2016;39(11):2065-2079.
Strasser B, Pesta D. Resistance training for diabetes prevention and therapy: experimental findings and molecular mechanisms. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:805217.
Liao WH, Chen JW, Chen X, et al. Impact of Resistance Training in Subjects With COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir Care. 2015;60(8):1130-1145.
Cornelissen VA, Fagard RH, Coeckelberghs E, Vanhees L. Impact of resistance training on blood pressure and other cardiovascular risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized, controlled trials. Hypertension. 2011;58(5):950-958.
Heiwe S, Jacobson SH. Exercise training in adults with CKD: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 2014;64(3):383-393.
彭渝森,腎臟病在台灣 (Retrieved from http://www.ntcma.org/98/twckd.pdf)
文章來源:Dr.史考特的一分鐘健身教室











